Selecting the right design for your BLDC motor is important.
The Difference: Axial vs. Radial Flux Motors
Electric motors can most commonly be classified into two categories based on their magnetic flux configuration: Radial Flux and Axial Flux.
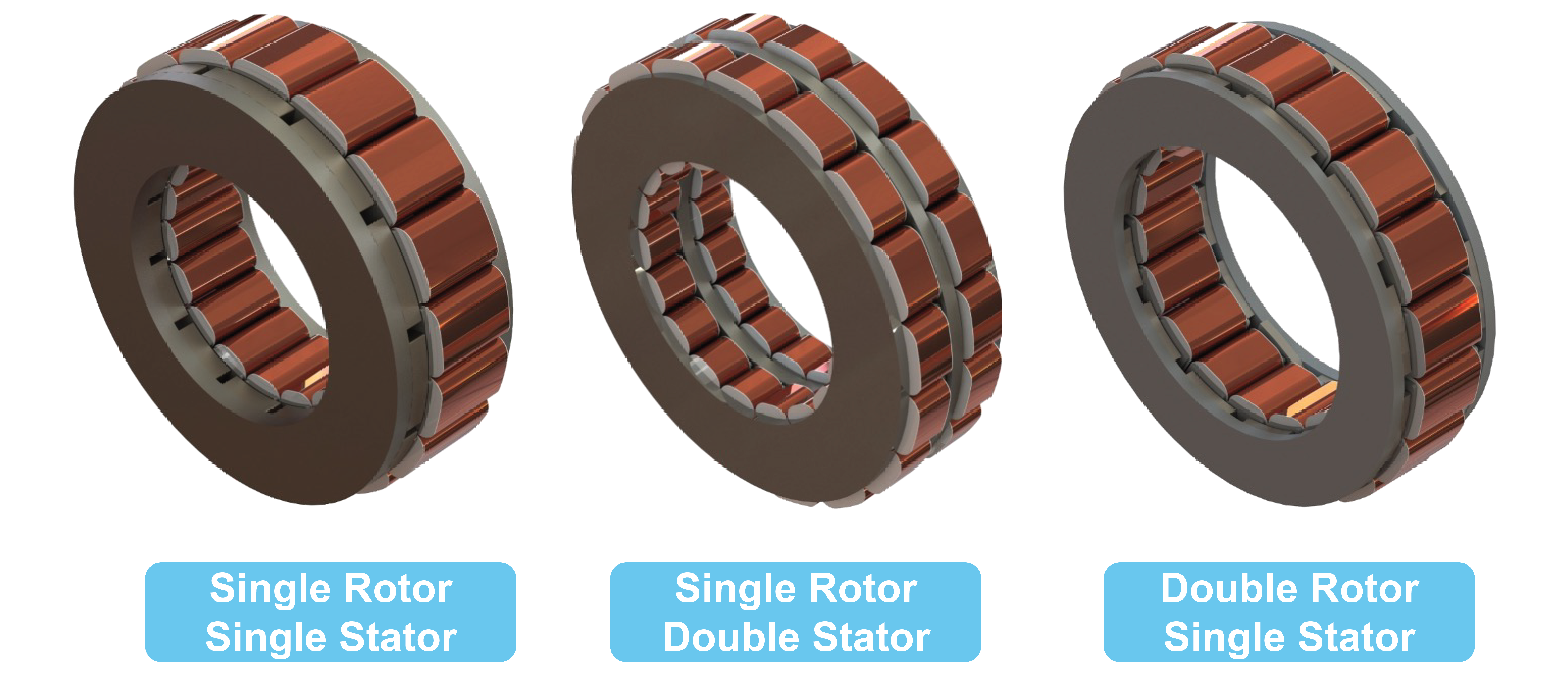
Radial Flux Motors
In radial motors, the magnetic flux flows radially, perpendicular to the motor shaft. These motors have a cylindrical design, with the rotor positioned inside or outside the stator, creating a more traditional, elongated shape. Meaning the OD of the motor is likely smaller than the overall length. These types of motors utilize traditional stamped laminations and can use various types of copper windings including hairpin windings.
Axial Flux Motors
On the other hand, axial motors have a magnetic flux that flows parallel to the motor shaft. This results in a flat and compact design. The structure consists of rotors and stators arranged in a disc-like configuration, allowing for more efficient use of space and materials Axial flux motors are also known as pancake motors because of their flat, compact shape and low length-to-diameter ratio.
Benefits of Axial Flux Motors
Higher Power Density
Axial flux motors can deliver 4 times the power density compared to radial flux motors. This makes them perfect for applications where space and weight are a pressing factor. The compact design not only saves space but also contributes to a lighter overall system, which is crucial in industries where every pound matters.
Improved Efficiency
The design of axial flux motors leads to reduced eddy current losses and higher efficiency. This means lower energy consumption and extended operational range for EV applications. The higher efficiency of axial flux motors translates to significant energy savings and better overall performance, which are critical factors in today’s competitive market.
Enhanced Cooling
The flat, disc-like structure of axial flux motors allows for cooling, which is essential for maintaining performance and longevity under high-power conditions. Thermal management is vital to prevent overheating, ensuring that the motor operates at optimal temperatures and extends its operational life. This feature is particularly beneficial in high-demand applications that require consistent and reliable performance.
Using Soft Magnetic Composites in Axial Flux Motors
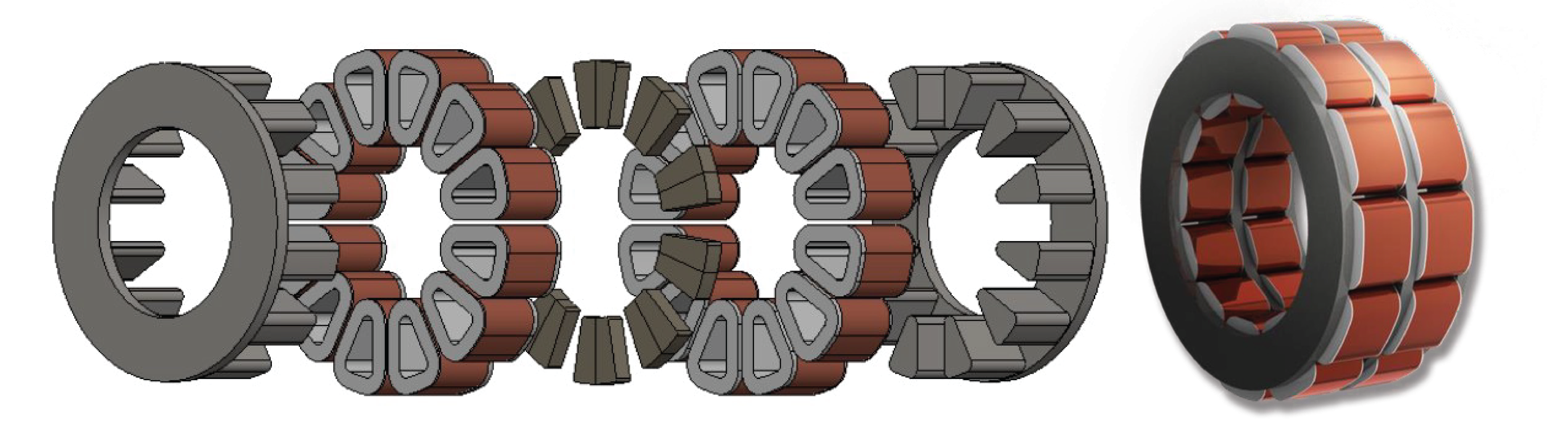
Soft magnetic composite (SMC) materials are key to unlocking the full potential of axial flux motors and have many advantages over traditional laminated cores. Made up of iron powder particles each coated with an electrically insulating layer Providing 3-dimensional flux vs the 2-dimensional flux of stacked laminations. Benefits of using SMC material in axial flux motors:
- SMC stator cores have smooth curved stator poles which facilitate pre-formed winding options taking advantage of a simplified assembly process thus lowering overall motor cost.
- The SMC process also brings a great advantage in tooth-to-tooth alignment and the vertical fill factor. These features allow the motor designer freedom to better utilize magnetic materials lowering weight which translates to cost.
