Innovative Solutions with Metal Injection Molding
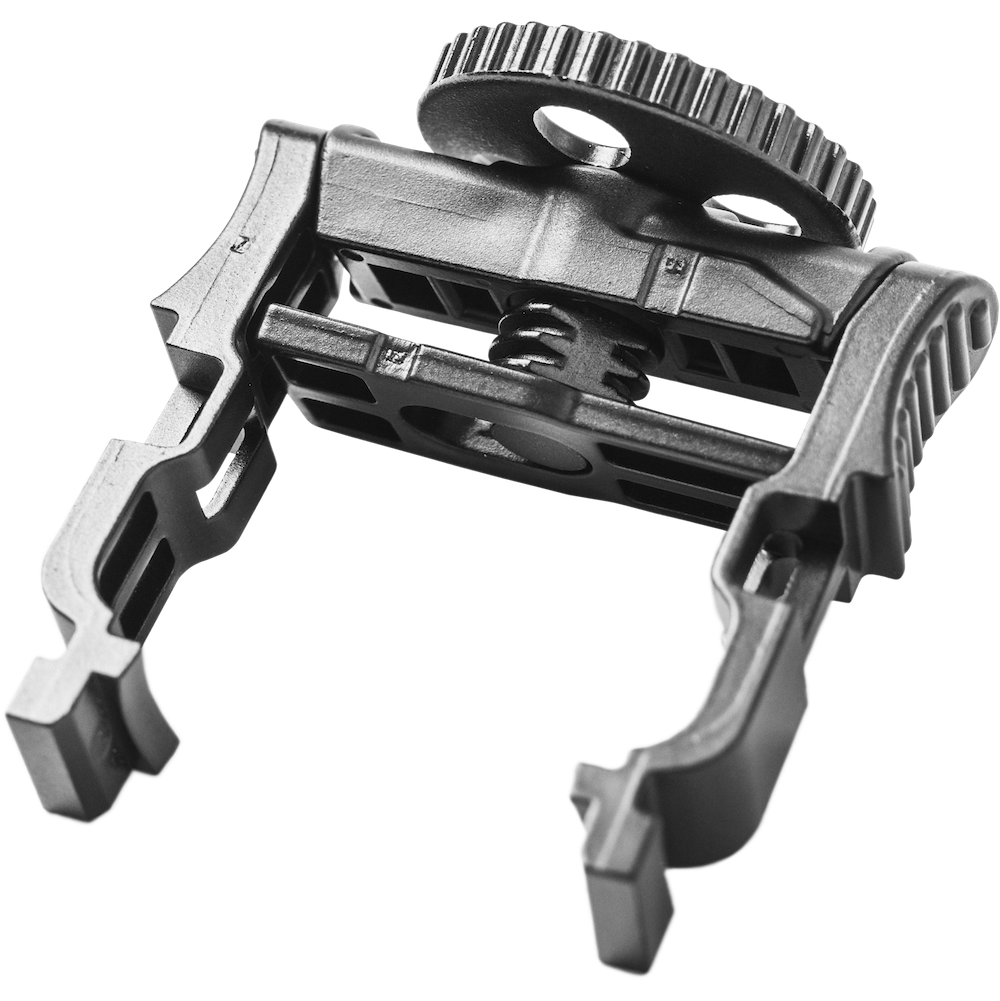
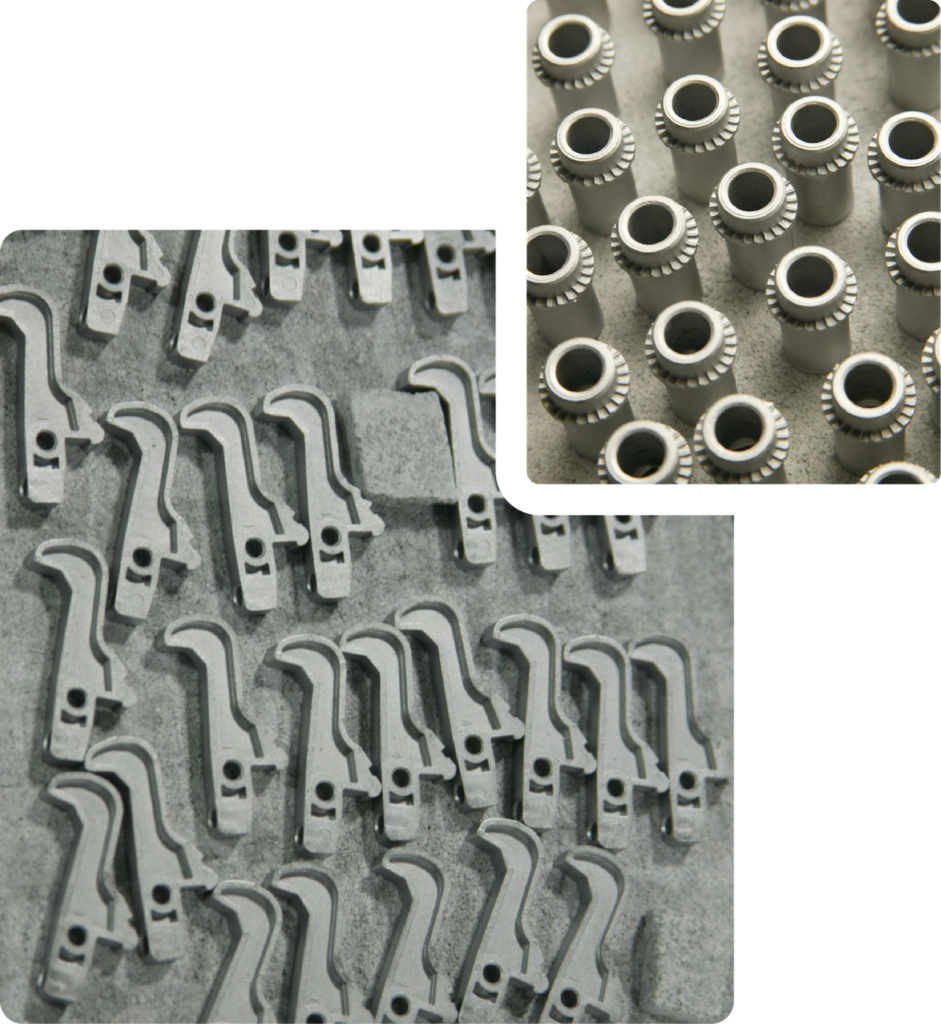

COST-EFFECTIVE SOLUTIONS FOR COMPLEX MANUFACTURING CHALLENGES
Enhancing Manufacturing Precision and Efficiency with Metal Injection Molding (MIM)
Confronted by the escalating costs and inherent limitations associated with conventional metal manufacturing technologies? Metal Injection Molding (MIM) emerges as a formidable alternative, integrating the design versatility of plastic injection molding with the structural integrity and durability of metal alloys. Particularly advantageous for sectors that require high precision, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, MIM offers a cost-efficient solution without compromising on quality.
Key Advantages of Metal Injection Molding:
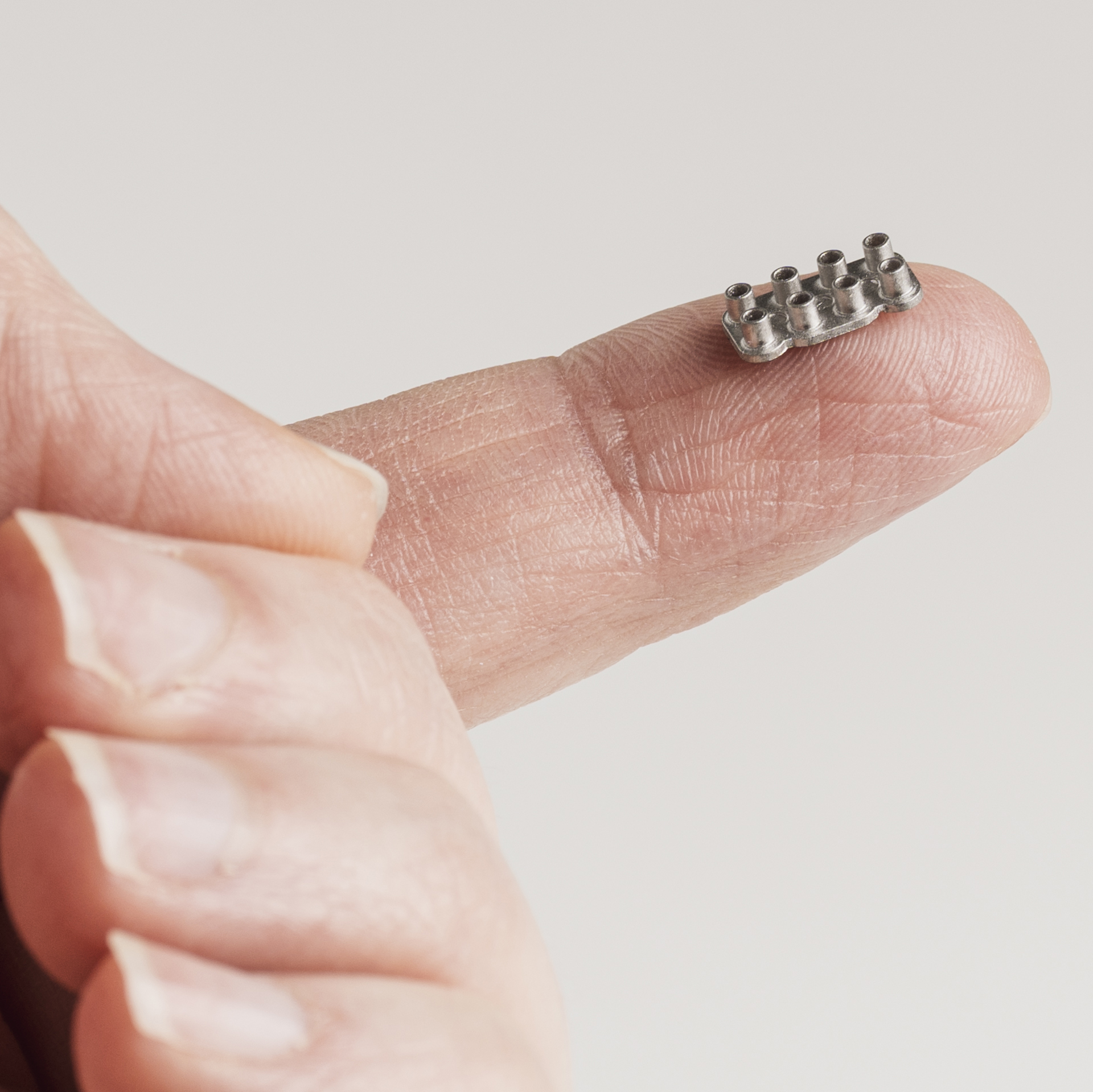
Complex Geometries: MIM excels in fabricating intricate designs that pose challenges for traditional metal forming methods, enabling the realization of detailed component features with high precision.
Material Efficiency: Through its near-net-shape production capabilities, MIM enhances material utilization, significantly reducing waste and thereby supporting cost reduction initiatives.
Sustainability: MIM contributes to sustainable manufacturing practices by minimizing material waste and energy consumption, aligning with environmental conservation goals
Consistency: The process ensures uniform quality across large production volumes, achieving high repeatability which is critical for maintaining standardization in product manufacturing.
Superior Mechanical Properties: MIM components exhibit enhanced durability and performance, tailored to meet the rigorous demands of specific applications.
Versatile Integration: Facilitates the integration of components into larger assemblies, as MIM parts can be readily joined or brazed, enhancing the overall structural coherence and functionality of the final product.
Discover the strategic benefits of incorporating MIM into your production line to streamline processes and achieve superior outcomes. Metal Injection Molding not only addresses the immediate manufacturing challenges but also enhances operational efficiencies and product performance across diverse industry applications
MIM Process
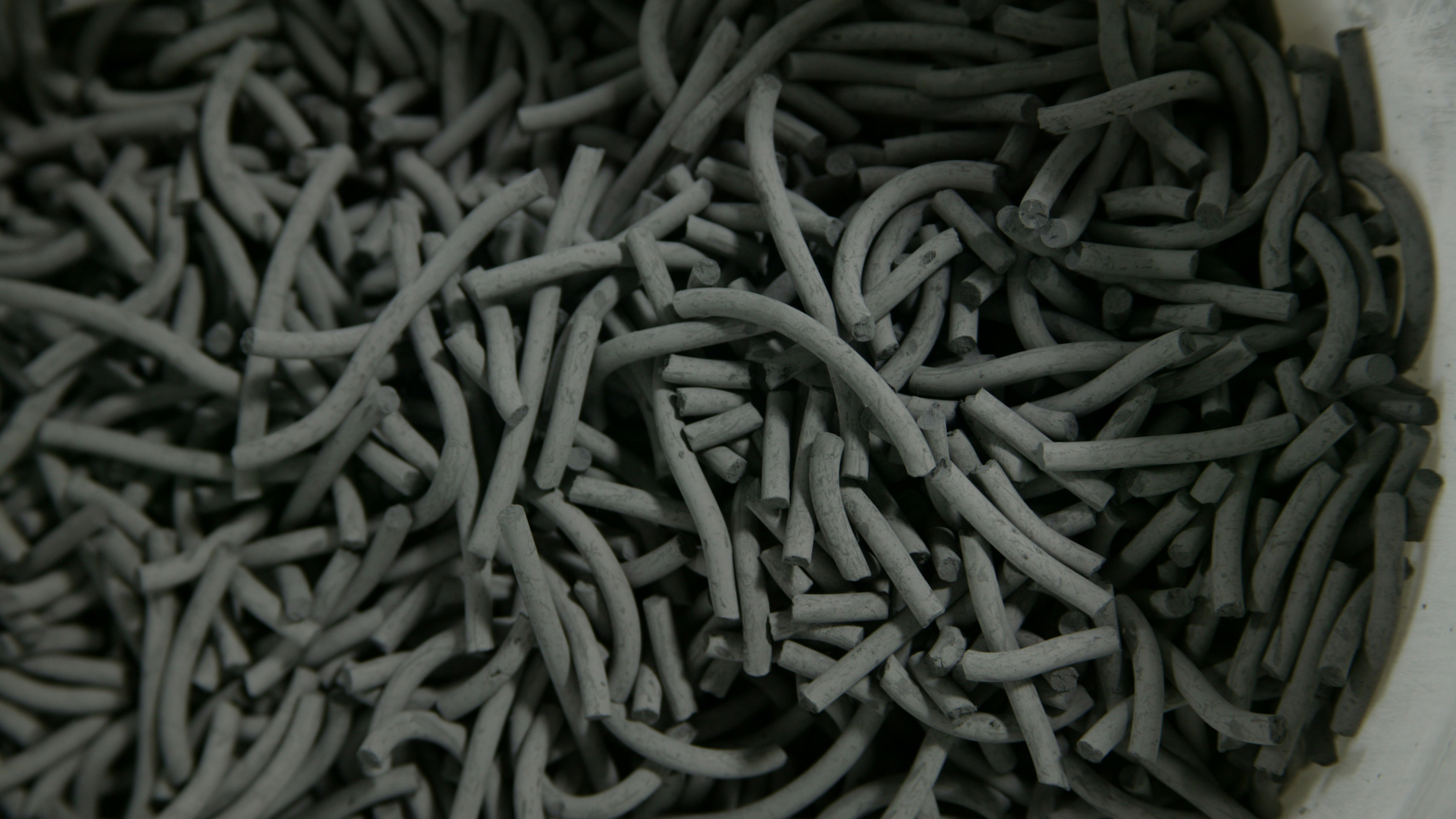

Compounding
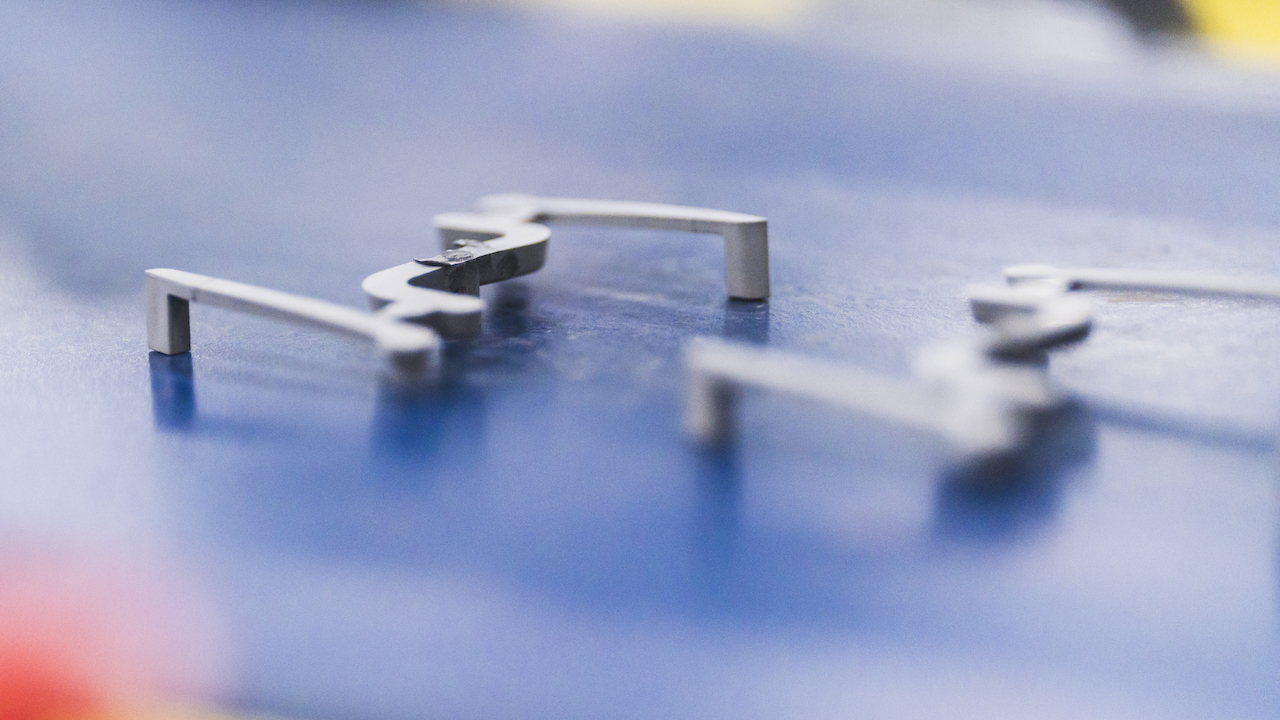

Injection
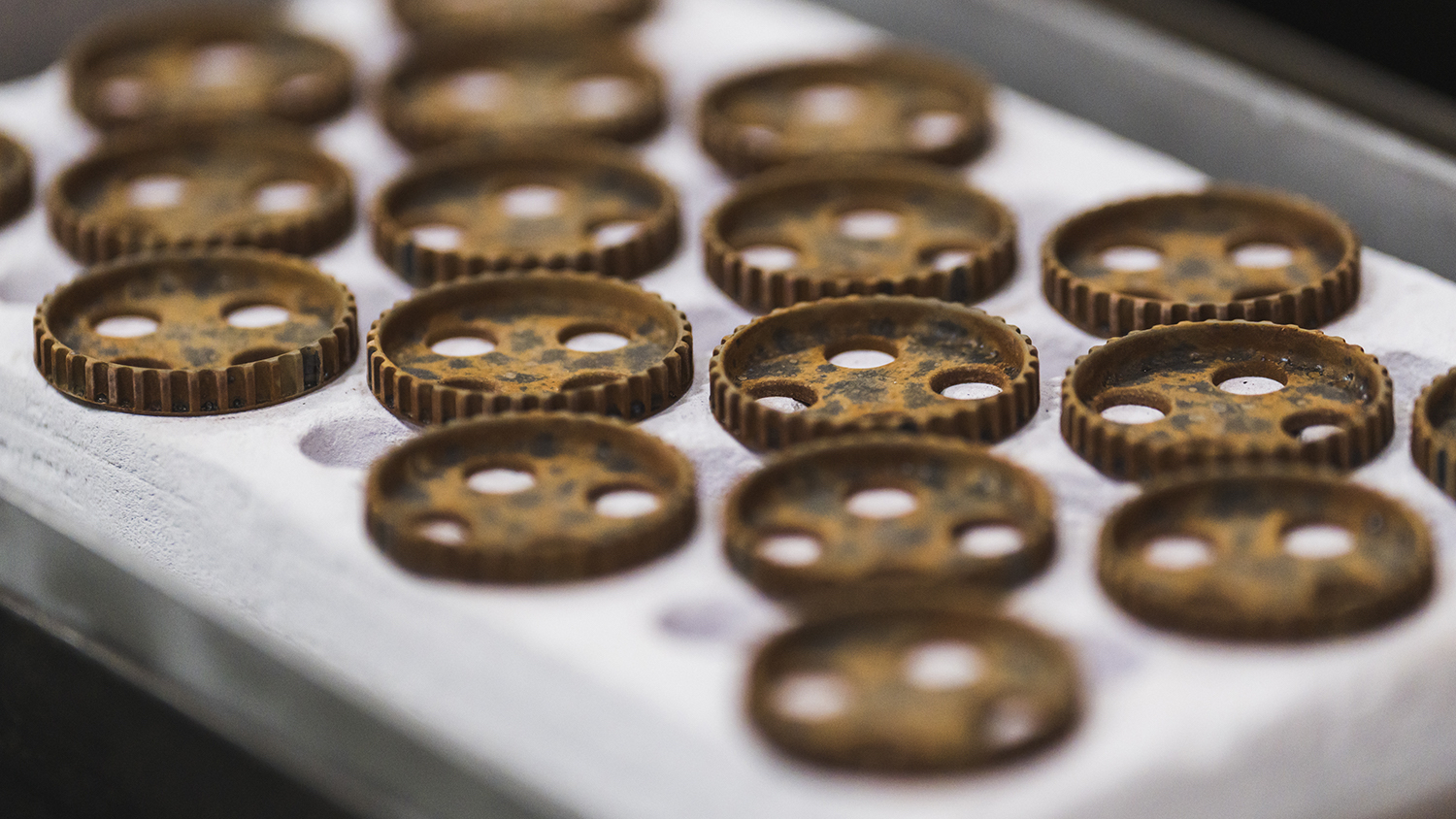

Debinding
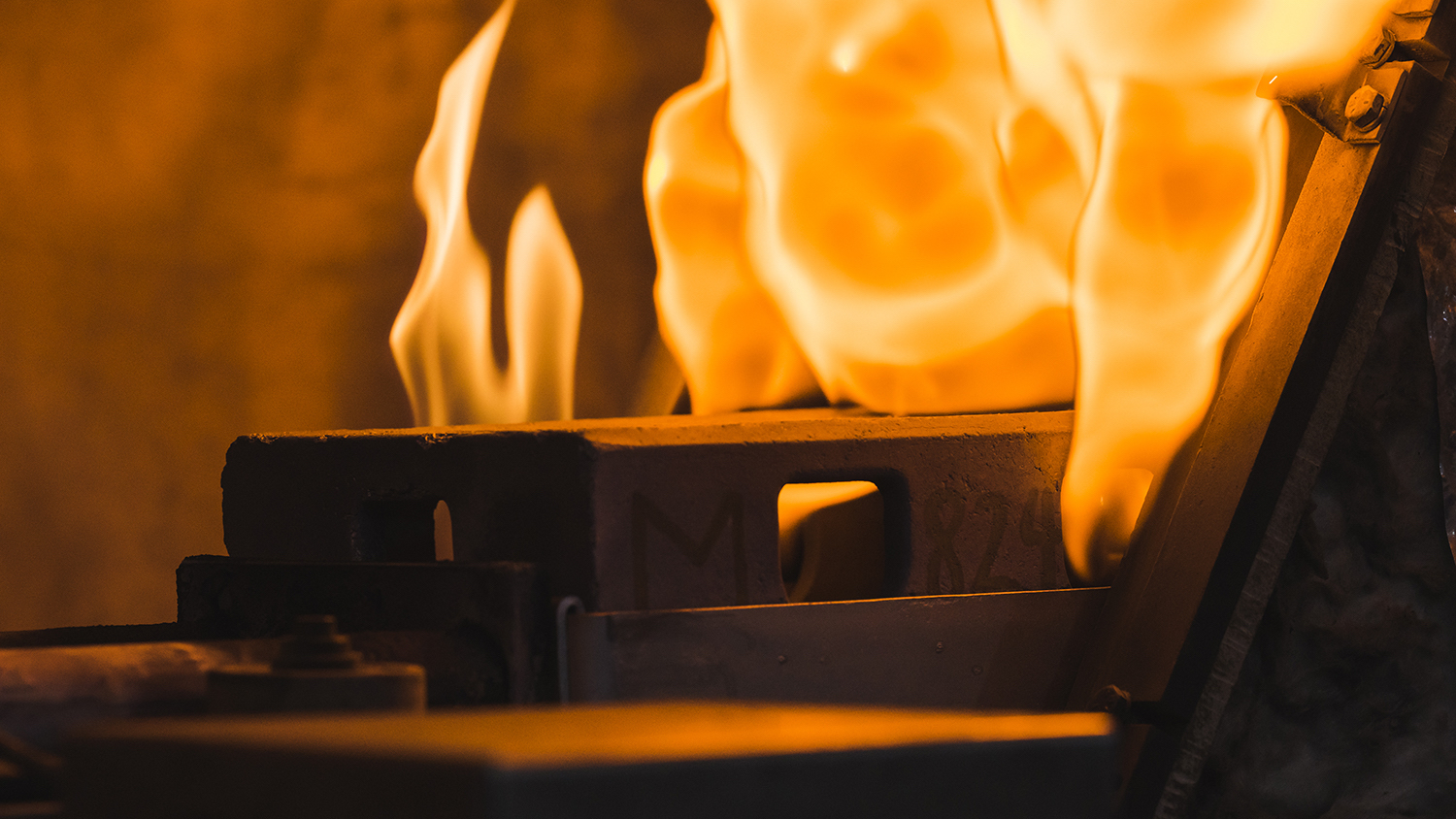

Sintering
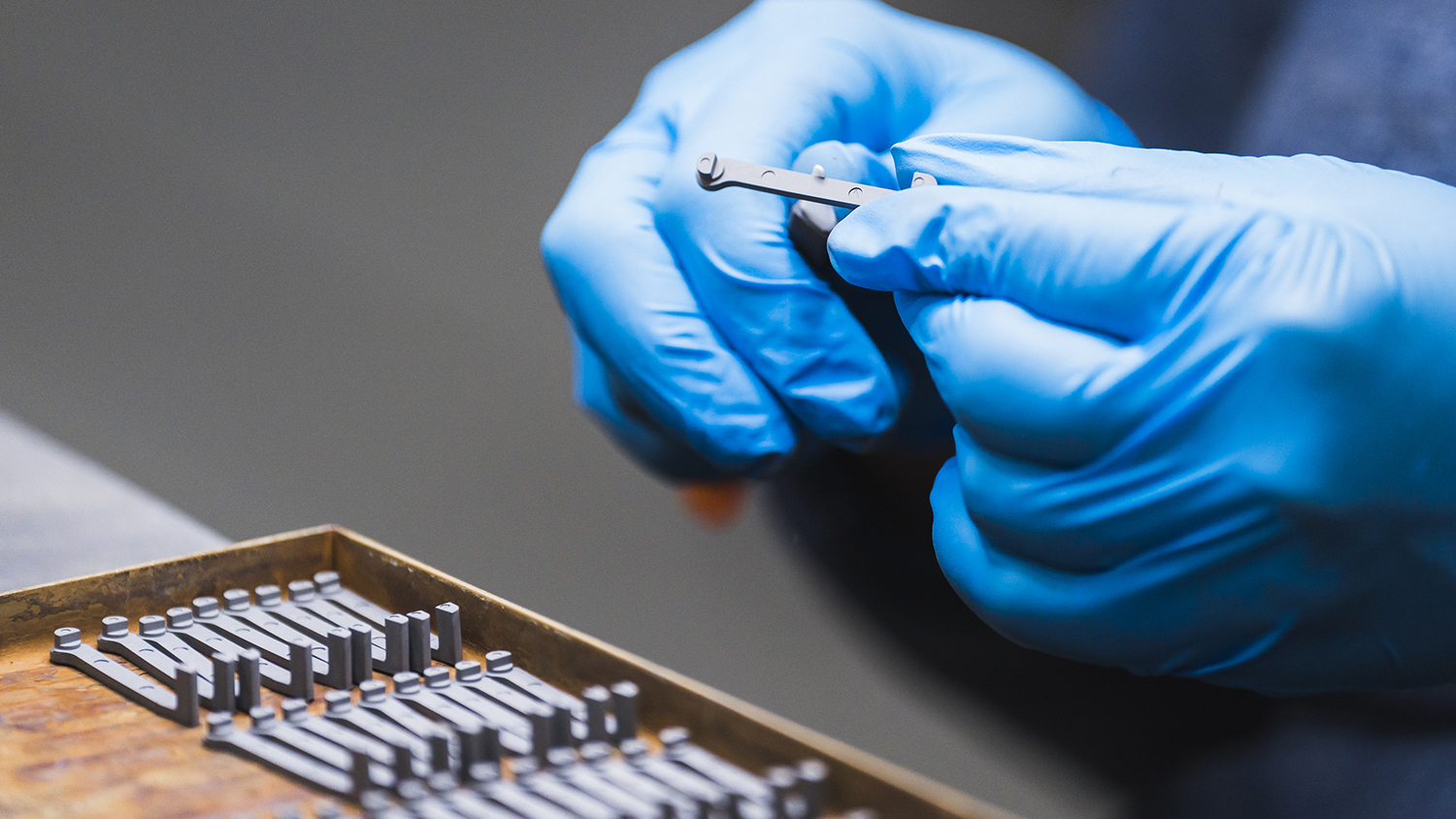

Secondary

Compounding

Injection

Debinding

Sintering

Secondary
Questions about our process?
What can MIM do?
MIM components excel in a variety of applications and markets.






Learn about our solutions across multiple industries.
MIM Materials and Alloys
The MIM process uses a wide array of alloys and metals. From stainless steel to tungsten alloy to low alloy steel, and more, MPP provides expertise in working with any material used in the MIM process. MIM is an excellent alternative to other forming processes, including Inconel casting for aerospace manufacturing.
The most commonly used elements in MIM processing are:
- Iron
- Nickel
- Chromium
- Molybdenum
Iron and nickel are two of the easiest elements to process because of their compatible melt temperature and ease of sintering. Iron and nickel make up a significant amount of the total tonnage produced in the industry.
MPP’S MOST POPULAR MIM MATERIALS
Superalloys
- A-286 – Excellent corrosion resistance, high temperature strength
- Hastelloy X – Good oxidation resistance, high temperature strength
- Inconel 625 – Excellent corrosion and heat-resisting characteristics
Stainless Steels
- 17-4PH – Best combination of strength and corrosion resistance
- 316 – Excellent corrosion resistance
- 420 – High hardness
Low Alloy Steels
- 2200 – Similar to PM FN-0200, good magnetic and toughness properties
- 4605 – High treatable, high-strength steel, up to HRC 52
- 4140 – Heat treatable, high-strength steel, up to HRC 60
Controlled Expansion Alloys
- Fe-Ni – The alloy composition (ie, Invar, Alloy 42, etc) can be tailored for the application’s thermal expansion requirement
- F15 – AKA Kovar®, the alloy is engineered for hermetic glass-metal seals
High Density Alloys
- W-based – High temperature sintering proficiency allows various tungsten-nickel-iron alloy capability; sintered densities range up to 18 g/cc
Soft Magnetic Alloys
- Fe-Si – Silicon content up to 9% allows for high resistivity with good soft magnetic response
- Fe-Co – Excellent magnet saturation properties